Mechanism of Evolution
Mechanism of Evolution: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Genetic Drift, Gene Flow, Directional Selection, Stabilising Selection, Disruptive Selection, Microevolution and, Mechanism of Evolution
Important Questions on Mechanism of Evolution
Newborn babies have smaller jaws is an example of microevolution.
The change in the _____ (RNA/allele) frequency for a particular period of time in a population is called microevolution.
The microevolution can be best defined as, the change in the allele frequency for a particular period of time in a population.
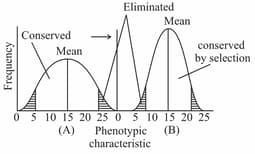
The bill sizes in a bird species of seed crackers from West Africa shows a bimodal distribution. Their most abundant food sources are two types of marsh plants that produce hard and soft seeds, consumed preferentially by the large and small billed birds, respectively. This bimodal distribution of bill sizes is a likely consequence of
_____ drift is most effective in small populations of organisms.
Which type of selection is a suitable example for industrial melanism? (Directional selection/Disruptive selection/ Facultative Selection)
The range of variation among population members for a trait determined by multiple genes is shown in the graph below.
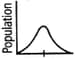
If the population is subjected to disruptive selection for several generations, the graph will be?
A type of natural selection that preserves existing allelic frequencies is called
In a random mating population in equilibrium, which of the following brings about a change in gene frequency in a non-directional manner
Random genetic drift in a population probably results from
Random genetic drift in a population probably results from